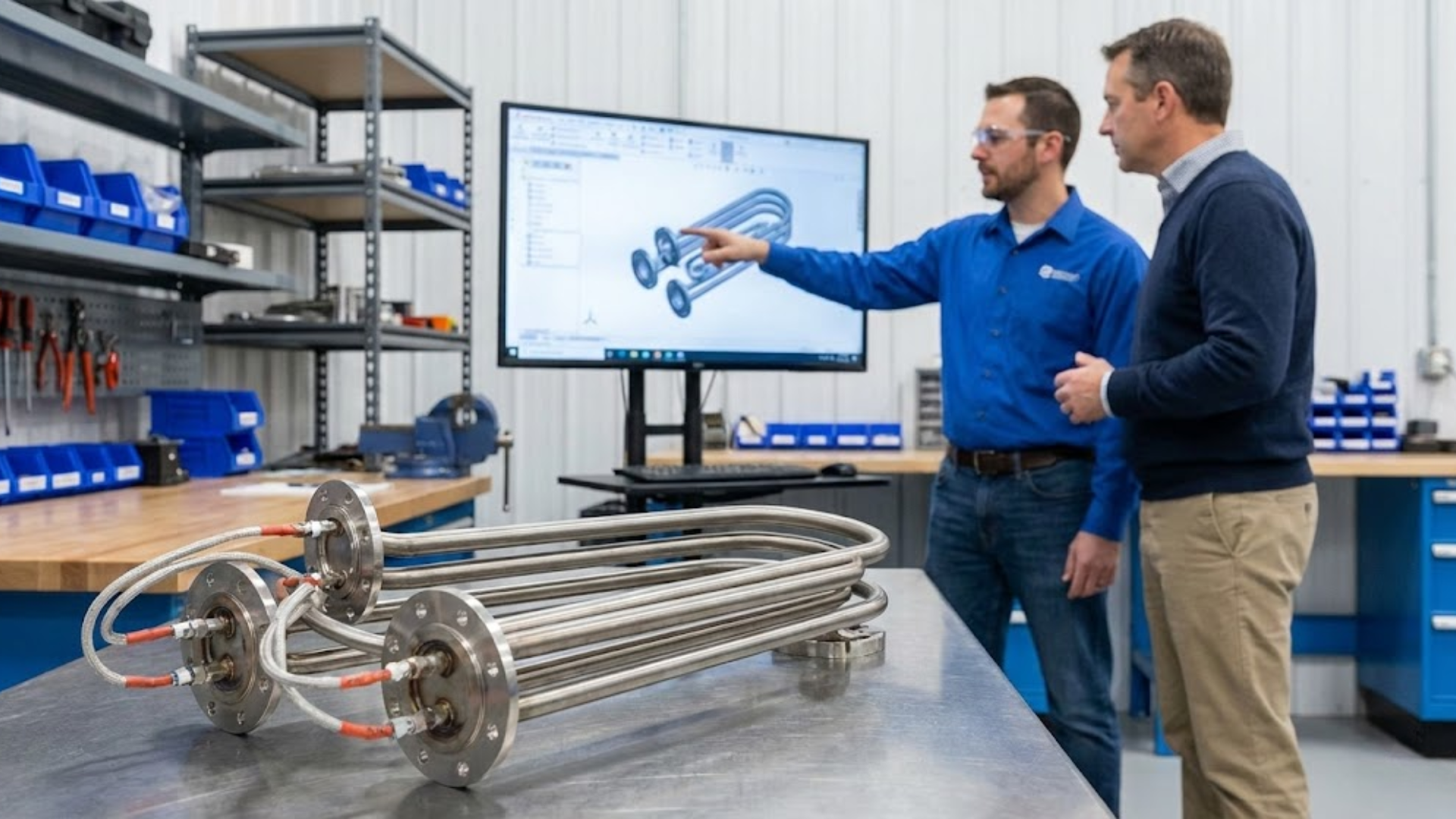
Choosing the right industrial electric heater is not a commodity decision. Heater selection directly affects system performance, safety, energy efficiency, maintenance frequency, and total lifecycle cost. When a heater is underspecified, mismatched to its environment, or poorly integrated, the result is premature failure, uneven heating, and unnecessary downtime.
For OEMs, engineers, and industrial operators, selecting the right heater requires evaluating real operating conditions, not just nameplate ratings. This guide outlines the key factors to consider when specifying an industrial electric heater and explains how to align the heater’s design with application requirements.
Define the Application and Heating Medium
The first step is understanding what you are heating and how heat is transferred. Industrial electric heaters are designed for heating media, most commonly air, liquids, or solid surfaces.
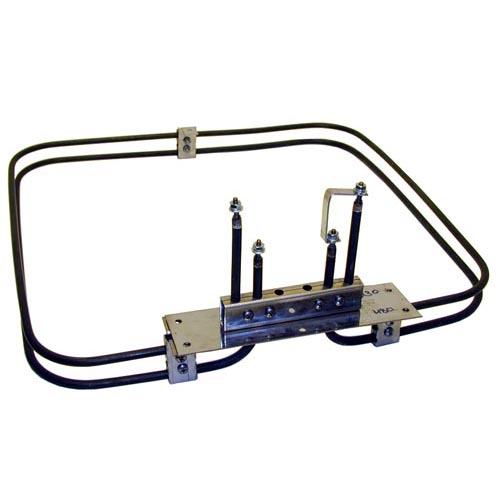
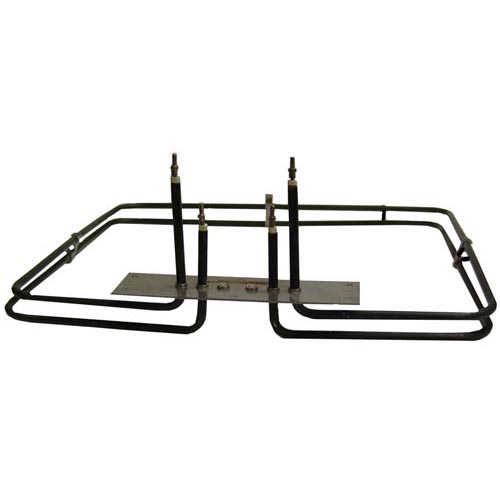
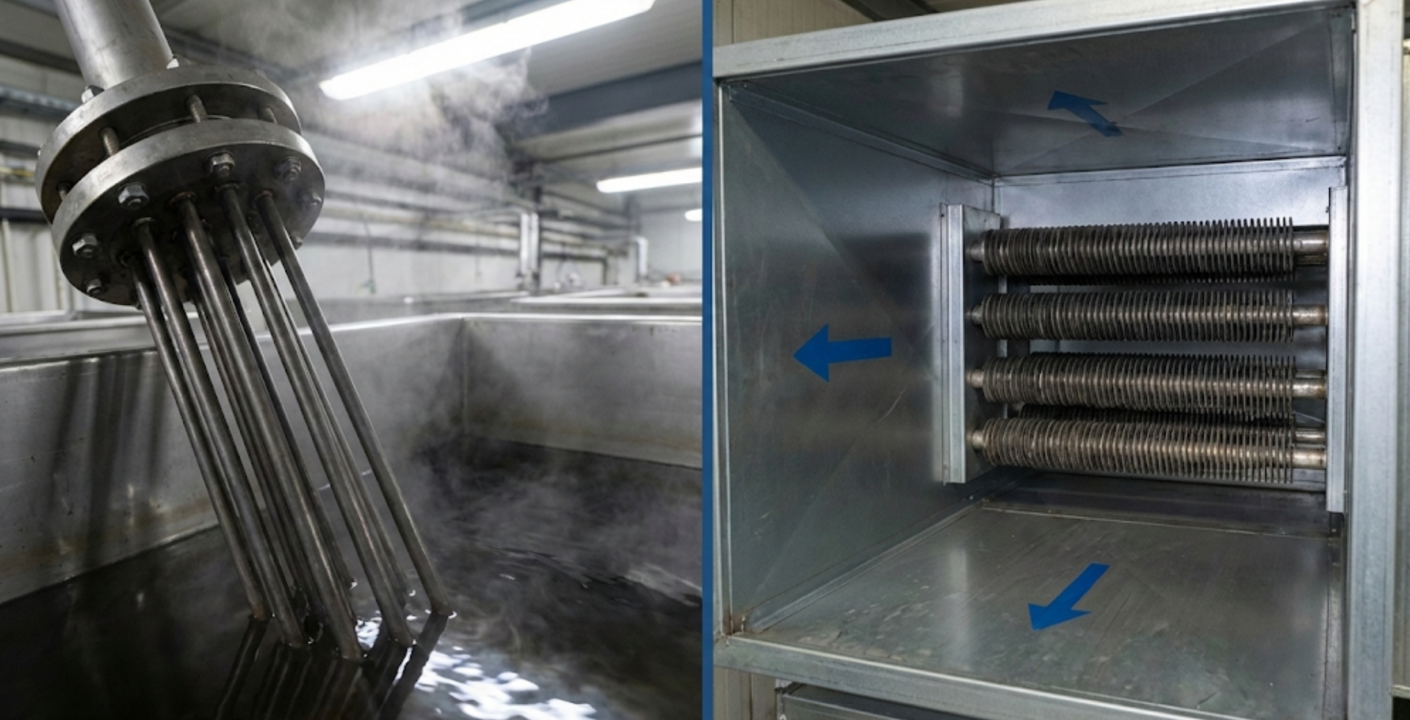
Applications involving airflow, such as industrial enclosures, process air systems, drying equipment, and HVAC-related systems, typically rely on open coil electric air heaters. These heaters transfer heat directly into moving air and offer fast thermal response when airflow is clean and controlled.
Selecting a heater without clearly defining the heating medium is one of the most common causes of poor performance and early element failure.
Select the Appropriate Heater Technology
Different heater technologies are engineered for different environments and operating conditions.
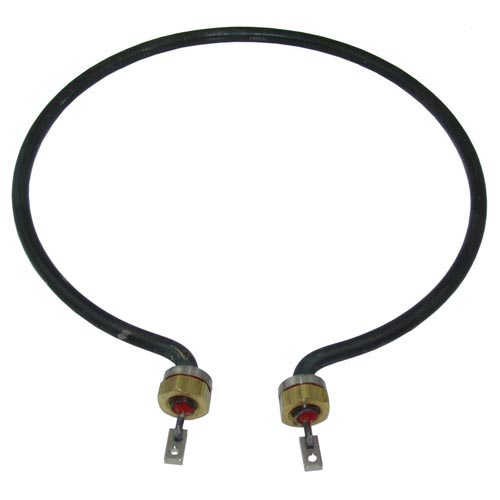
Open coil heaters are ideal for air heating applications where efficiency and responsiveness are required. Tubular and finned tubular heaters are better suited for environments with dust, moisture, or airborne contaminants where additional element protection is necessary. Immersion heaters are designed specifically for liquid heating and should only be used where proper fluid contact and cooling are guaranteed.
Matching heater technology to the application environment is critical to long-term reliability.
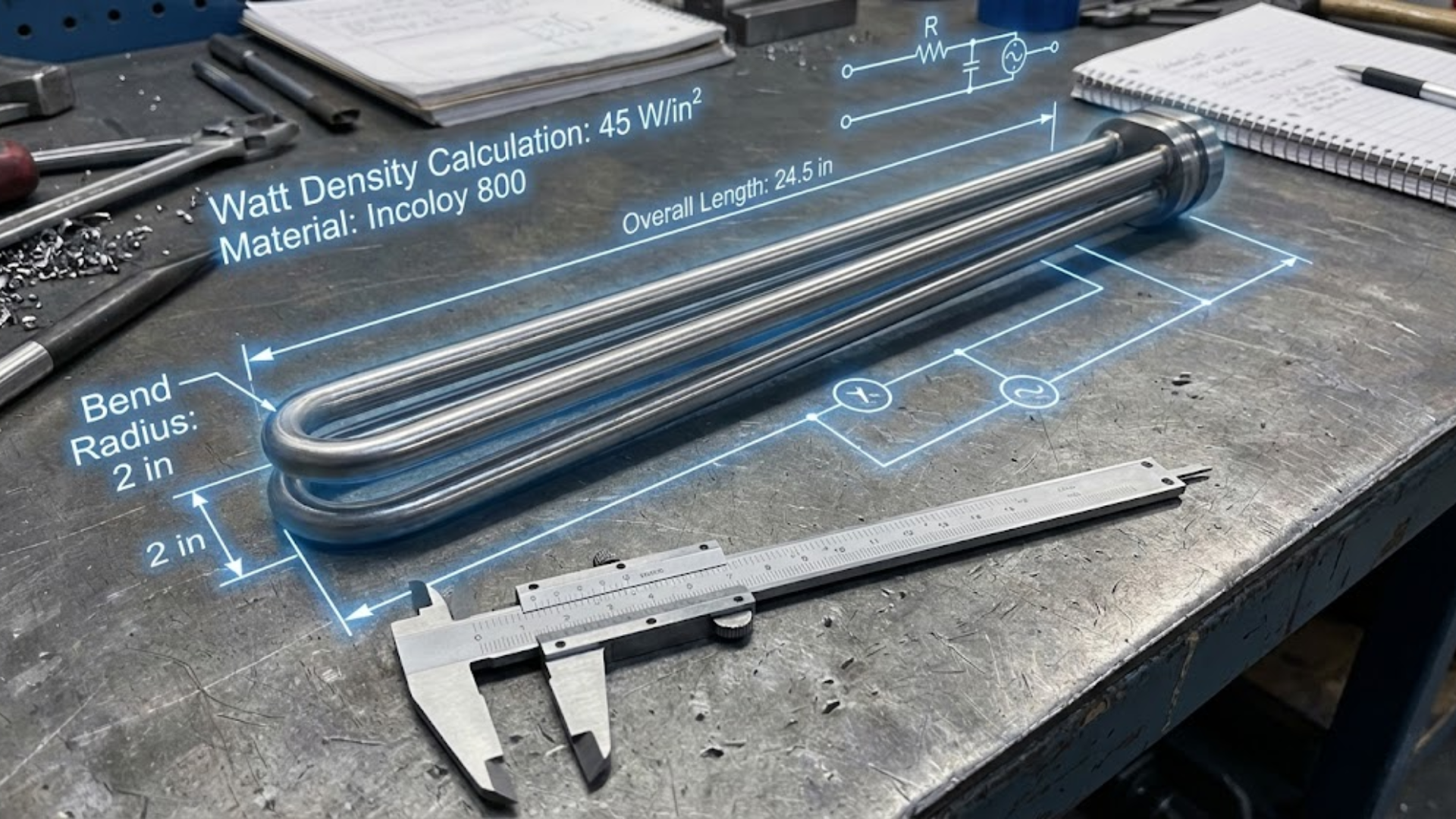
Determine Required Wattage and Watt Density
Heater performance is governed by total wattage and watt density.
Wattage determines how much heat energy the heater can deliver, while watt density determines how concentrated that heat is on the heating element. Excessive watt density can cause overheating and shorten heater life, especially in applications with inconsistent airflow or heat dissipation.
Accurate heater sizing requires calculating the thermal load based on airflow or mass, desired temperature rise, heat losses, and duty cycle. Proper sizing improves energy efficiency and reduces stress on the heating element.
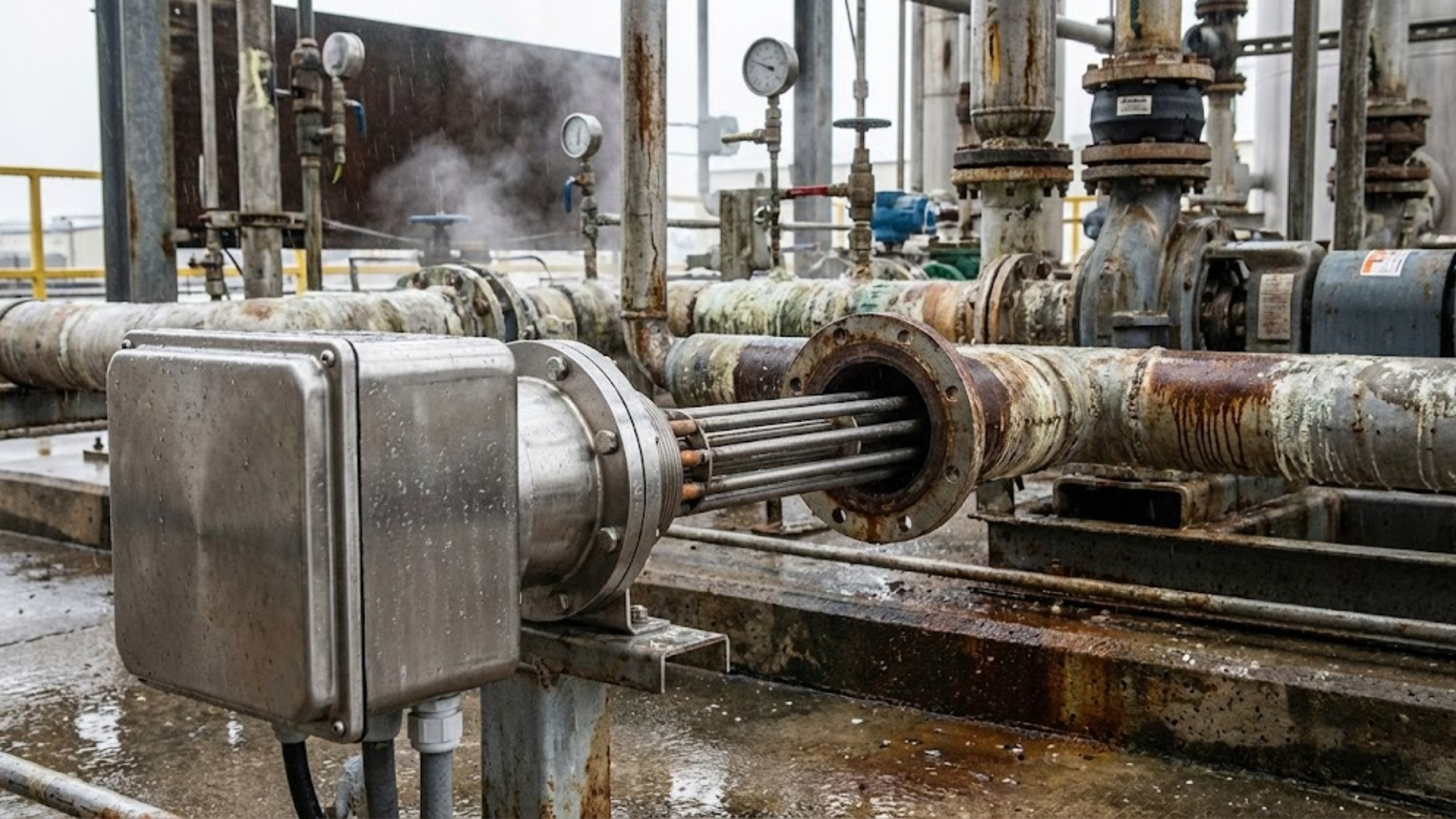

Industrial environments expose heaters to vibration, thermal cycling, moisture, corrosion, and airborne contaminants. These factors must influence material selection and construction.
Frame materials, support structures, and insulation systems should be chosen based on operating temperature, exposure conditions, and expected service life. Stainless steel, aluminized steel, and specialty alloys are commonly used depending on corrosion resistance and thermal requirements.
Ignoring environmental conditions often results in heaters that meet specifications on paper but fail prematurely in service.
Confirm Electrical and Control Compatibility
Industrial electric heaters must be compatible with the facility’s power infrastructure. This includes voltage, phase configuration, and current capacity. Many industrial applications require three-phase heaters for load balancing and efficiency.
Temperature control and safety are equally important. Integration with thermostats, sensors, or closed-loop control systems improves stability and reduces thermal stress. Over-temperature protection and proper grounding should always be part of the heater specification.
Consider Maintenance and Lifecycle Cost
Upfront cost is only one part of the equation. Maintenance access, ease of service, replacement frequency, and downtime all impact the total cost of ownership.
Heaters designed with proper support systems, conservative watt density, and accessible terminals typically offer longer service life and reduced maintenance burden. In industrial environments, reliability and uptime often outweigh initial cost savings.
Work With an Industrial Electric Heater Manufacturer Early
For custom or application-specific requirements, working directly with an experienced industrial electric heater manufacturer improves outcomes. Early collaboration allows heater design to align with actual operating conditions rather than assumptions.
Creative Assemblies supports heater selection through engineering guidance, custom manufacturing, and application-driven design. Their Electric Heater Design Consulting services help ensure heaters are built for performance, manufacturability, and long-term reliability.
Custom heater assemblies also reduce installation complexity and help OEMs move from prototype to production with fewer design revisions.
Final Heater Selection Checklist
Before finalizing a heater specification, confirm the following:
- The heating medium and method are clearly defined
- Heater technology matches environmental conditions
- Wattage and watt density are correctly calculated
- Materials are suitable for exposure and the temperature range
- Electrical compatibility and controls are confirmed
- Maintenance and lifecycle costs are considered
- Manufacturer support is involved for custom applications
Selecting the right industrial electric heater is a technical decision that rewards careful planning. When heater design aligns with application realities, the result is improved reliability, lower operating costs, and consistent system performance.
For application-specific guidance or custom heater solutions, contact Creative Assemblies directly.